Transport and Communication in India
Introduction
- Transport and Communications play a vital role in the economic development of India. Transport system helps with the easy movement of human beings and materials.
- It acts as the arteries and veins of national development.
- The transport system is of four types.
- Roadways, Railways, 3. Waterways and 4. Airways.
Roadways

- Roads play an important role in carrying goods and passengers for short, medium and long distances.
- It is highly suitable for short distance services. It is comparatively easy and cheap to construct and maintain roads.
- Road transport system can establish easy contact between farms, fields, factories and markets and can provide door to door transport services.
- Roads are the most universal mode of transport. Indian roads are cost efficient. It is used by all sections of people in the society.
- India has the second longest road network in the world with a total length of 56,03,293 km as of 2016.
- About 85% of passengers and 70 % of freight traffic are carried by roads every year.
- For the purpose of construction and maintenance, roads are classified into National Highways (NH), State Highways (SH), District Roads, Rural Roads (Village roads), Border Roads and International Highways.
Classification of Roads in India
National Highways (NH)
- National Highways form the most important system of road transportation in India. These highways are running through length and breadth of the country connecting capitals of states, major Ports, rail junctions, industrial and tourist centres.
- Ministry of Road Transport and Highways of India,is responsible for the development and maintenance of National Highways in India.
- The total length of the National Highways (NHs) in India is 1,01,011 km which accounts for 1.8 % of the total road network length in 2016.
- The longest National highway is NH-7 which runs from Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh to Kanniyakumari in Tamil Nadu covering a distance of 2369 km.
- The shortest national highway is NH-47A, which runs from Ernakulum to Kochi port (Willington Island) covering a distance of 6 km.
State Highways
- The state highways are usually roads that link important cities, towns and district headquarters within the state and connect them with national highways or highways of neighbouring states.
- These roads are administered and financed by state governments. State Highway runs to the length of 1, 76,166 km as of 2016.
District Roads
- District Roads provide connectivity between the district and taluk headquarters with the state highways and national highways.
- District Roads are constructed and maintained by the Public Works Department of the states. The total length of the road of this category is 5,61,940 km(16.81%) in 2016.
Rural Roads (Village Roads)
- Rural roads connectivity is a key component of rural development. These roads are vital for providing links in the rural areas.
- It links the different villages with their neighbouring towns. They are maintained by Village Panchayats.
- The total length of rural roads in India is 39,35,337 km as of 2016.
- Rural roads consist of Panchayat roads, (ZillaParishad, PanchayatSamiti, GramPanchayat);roads of the PradhanMantri Gram SadakYojana (PMGSY) and those constructed by the State PWDs.
Border Roads

- These are the roads of strategic importance in border areas. They are constructed and maintained by Border Roads Organization.
- It was established in 1960 for the development of the roads of strategic importance in the northern and northeastern border areas.
- Border Roads Organization has constructed world’s highest road joining Chandigarh and Leh in Ladakh. This road runs at an average altitude of 4,270 meters.
Golden Quadrilateral
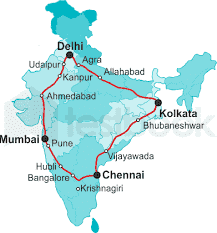
- 5,846 km long road of 4/6 lanes connecting, India’s four metropolitan cities: Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai-Delhi. This project was launched in 1999.
North–South and East-West Corridors
- NorthSouth corridor aims at connecting Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir with Kaniyakumari in Tamil Nadu (including Kochi-Salem Spur) with 4,076km long road.
- The East-West corridor has been planned to connect Silchar in Assam with the port town of Porbandar in Gujarat with 3,640kmof road length. The two corridors intersect at Jhansi.
Expressways

These are multi-lane good quality highways for high speed traffic. Some of the important expressways are
- Mumbai-Pune Road
- Kolkata-Dumdum Airport road
- Durgapur-Kolkata road
- Yamuna expressway between Delhi and Agra.
International Highways

- These are the roads that link India with neighbouring countries for promoting harmonious relationship with them.
- These highways have been constructed with an aid from world bank under an agreement with the Economic and Social Commission for Asia-Pacific (ESCAP).
- These roads connect important highways of India with those of the neighbouring countries such as Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and Myanmar.
- In India the densest road network is found in the northern plains where it is relatively easy to construct roads.
- In mountainous area, it is quite difficult to construct roads. Road density is the highest in Kerala and lowest in Jammu &Kashmir.
Railways

- Indian railway system is the main artery of the country’s inland transport. Railways cater to the needs of large scale movement of traffic, both for freight and passenger, thereby contributing to economic growth.
- Railways are considered as the backbone of the surface transport system of India. It promotes national integration by bringing people together. It also promotes trade, tourism, education etc.
- Railways help in the commercialization of the agriculture sector by facilitating the quick movement of perishable goods.
- Its role in transporting raw materials to industries and finished goods to markets is invaluable.
- Indian railways network is the largest in Asia and second largest in the world. The length of Indian railways network as of 2017 is 67,368 km with 7,349 railway stations. For operations and management, the Indian Railways is organized into 17 zones.
- Northern Railway – Delhi
- NorthWestern Railway – Jaipur
- North-Central Railway- Allahabad
- North-Eastern Railway – Gorakhpur
- North-East Frontier Railway – Guwahati
- Eastern Railway – Kolkata
- East coast Railway – Bhubaneswar
- East-Central Railway – Hazipur
- West-Central Railway – Jabalpur
- Central Railway – Mumbai (VT)
- Western Railway – Mumbai (Churchgate)
- Southern Railway – Chennai
- South Central Railway – Secunderabad
- South Eastern Railway – Kolkata
- South-Western Railway – Hubball
- South East Central Railway – Bilaspur
- South Coast Railway – Visakhapatnam
- The Northern Railway accounts for the longest route length, followed by the Western Railway. On the basis of width of the track, the Indian railways fall under four categories.
- Broad gauge with a width of 1.676 meter, Meter gauge with a width of 1 meter and Narrow gauge with a width of 0.762 meter and Light gauge with 0.610 meter.
- In recent times, many developments have taken place in the Indian railways. The arrival of Konkan Railway Corporation (KRC), Mass Rapid Transit System (MRTS), Metro and Sub-Urban railways provide easy and efficient means of transport.
- These are very helpful in avoiding traffic congestion and over crowding in urban areas.
Konkan railway

- One of the important achievements of Indian Railways has been the construction of Konkan Railway in 1998.
- It connects Roha in Maharashtra to Mangaluru in Karnataka and the track measures 760 km.
- It is considered as an engineering marvel. On its routes, the railway crosses 146 rivers and streams, nearly 2000 bridges and 73 tunnels.
- Asia’s longest tunnel nearly 6.44 km long is in this route. The states of Maharashtra, Goa and Karnataka are partners in this undertaking .
- The rail link between Banihal in Jammu region and Qazigund in Kashmir valley was opened in 2013.
- This rail line passes under the PirPanjal Range through a 11.2 km long tunnel.
Metro Railways in India

- There are 8 cities with metro rail connectivity in India. They are Kolkata (West Bengal), Chennai (Tamil Nadu), Delhi, Bengaluru (Karnataka), Gurgaon (Haryana), Mumbai (Maharashtra), Jaipur (Rajasthan) and Kochi (Kerala).
- The metro in Kolkata is the first one in India. It is also called as Mass Rapid Transit System (MRTS).
- As of September 2018, India has 507 km of operational metro lines and 381 stations.
Pipeline transport

- Pipelines provided a very convenient mode of transport to connect oil and natural gas fields, refineries and to the markets.
- In the past, these were used to transport water to cities and industries. Now solids can also be transported through a pipeline when converted into slurry.
- The initial cost of laying pipeline is high but subsequent running cost is minimum. It can be laid through difficult terrain as well as under water.
- It ensures steady supply of goods and reduces the transshipment losses and delays are the major advantages of pipeline transport.
- Oil field in upper Assam to Kanpur, from Salaya in Gujarat to Jalandhar in Punjab and gas pipeline from the Hazira in Gujarat otJagadispur in Uttar Pradeshare the three important network large network of pipeline in the country.
Waterways

- A waterway is an important mode of transport for both passenger and cargo traffic in India. It is the oldest and also the cheapest means of transport and most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky materials from one country to another.
- It is a fuel-efficient and eco-friendly mode of transport. The water transport is of two types- Inland Waterways and Ocean water ways (sea routes).
Inland Waterways
- India has an extensive network of inland waterways in the form of rivers, canals, lakes and backwaters.
- It depends upon the depth and width of the waterways and the continuity of the water flow.
- The total navigable length of our country is 14,500 km, out of which about 5,200 km length of rivers and 4,000 km length of canalscan be used by mechanized crafts. The total cargo carried by inland waterways is just about 0.1% of the total inland traffic of India.
- For the development, maintenance and regulation of national waterways in the country, the Inland water ways Authority was setup in 1986.
- The major national waterways are: National Waterway
- It extends between Haldia and Allahabad, measures 1620 km and includes the stretches of the GangaBhagirathi-Hooghly river system. National Waterway
- This waterway includes the stretch of the Brahmaputra river between Dhubri and Sadiya a distance of 891 km. National Waterway
- This waterway extends between Kollam and Kottapuram in the state of Kerala.
- It is the first national waterway in the country with 24 hour navigation facilities along its entire stretch of 205 km.
Oceanic Routes
- Oceanic routes play an important role in the transport sector of India’s economy. About 95% of India’s foreign trade by volume and 70 percentby value moves through ocean routes.
- Coastal shipping plays an important role in transport of bulk goods in India. Shipping is not only the most economical mode of transport, it is also an environment friendly mode.
- The sea and oceanic routes are mainly used for international trade and are connected through ports.
- There are 13 major and 200 minor or intermediate portsin India. The major ports are administered by the Central Government and minor ports are managed and administered by various state governments.
- The major ports on the east coast are Kolkata (including Haldia Dock), Paradip, Visakhapatnam, Chennai, Ennore and Tuticorin.
- The major ports on the west coast are Kandla, Mumbai, NhavaSeva (Jawaharlal Nehru Port), New Mangalore, Marmagao and Kochi. India has four major shipyards.
- Hindustan shipyard in Vishakhapatnam, Garden Reach workshop in Kolkata, Mazagaon Dock in Mumbai, Kochi Shipyard in Kochi.
- India is the second largest ship owning country in Asia and ranks 16th in the World.
Air Transport

- Airways are the quickest, costliest, most modern and comfortable means of transport, Air transport facilitates connectivity on a national, regional and international scale. It has made accessibility easier by connecting difficult terrains like high mountains and sandy deserts.
- It carries passengers, freight and mail. Air transport plays a key role in times of emergency as well as in the event of natural and man-made calamities like floods, epidemics and wars.
- Air transport in India made a beginning on 18th February, 1918when Henry Piquet carried a mail from Allahabad to Naini.
- In 1953, eight different airlines which were in operation in the country were nationalised.
- Domestic Airways fly within the boundaries of a country and International Airways connect major cities of the world.
- The Indian Air lines and Air India are the two airline services run by the government of India.
- Indian Air lines provides the domestic air services and Air India provides international air services.
- Presently, there are 19 designated international airportsavailable in the country. These airports are managed by Airports Authority of India.
- Some of them are NetajiSubhash Chandra Bose International Airport, Kolkata, Chennai International Airport, Chennai, Indira Gandhi International Airport, Delhi, ChhatrapatiShivaji International Airport, Mumbai, Thiruvananthapuram International Airport, Thiruvananthapuram, SardarVallabhBhai Patel International Airport, Ahmedabad, Bangalore International Airport, Bengaluru, Rajiv Gandhi International Airport, Hyderbad etc.
- Besides this, there are about 80 domestic airports and about 25 civil enclaves at defence air fields.
Pavan-Hans Helicopter Ltd

- Pavan-Hans Helicopter Ltd has been providing Helicopter support services to the petroleum sector, including ONGC and oil India Ltd.
- It is a public sector company based in New Delhi. Its operations are based at the Juhu Aerodrome in Vile Parle (West) Mumbai.
- Pavan-Hans is a Mini Ratna–I category public sector undertaking.
- It often provides services to various state governments in India particularly north east India Inter Island, Ferry services in Andaman & Nicobar Islands, services to Lakshadweep Island etc.
Airports Authority of India (AAI)

Airports Authority of India (AAI) was constituted in 1995. It provides security to Indian Airports. AAI under the ministry of Civil Aviation is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining and managing civil aviation infrastructure in India.
Communication
Communication is a process that involves exchange of information, thoughts and ideas. Technology does wonders in communication fields. Communication is categorized in to personal and mass communications./
Personal Communication
- The exchange of information between the individuals is called personal communication. It includes post and telegraph services, telephone, mobile phone, short message services, fax, internet, e-mail
- Personal Communication system enables the user to establish direct contact. The Indian postal network is the largest in the world with 1,55,000 post offices.
- Of these more than 1,39,000 post offices are located in rural areas. The postal service was opened to the public in the country in
- The first Indian postal stamp was issued in 1852 in Karachi.Collecting and delivering mail is the primary function of the department of posts. It introduced the Quick Mail Service in 1975 and today it covers the entire country.
- The Quick Mail Service functions on the basis of the system of PIN (Postal Index Number) code which was introduced in 1972.
- The premium products include the Money order, e-money order, Speed Post, Express Parcel Post, Business Post, Media Post, Satellite Post, Retail Post, Greeting Post, Data Post, Speed Net and Speed Passport Services.
- Cards and envelopes are considered firstclass mail and are airlifted between stations covering both land and air.
- The secondclass mail includes book packets, registered newspapers and periodicals. They are carried by surface mail, covering land and water transport.
- To facilitate quick delivery of mails in large towns and cities, six mail channels have been introduced recently.
- They are called Rajdhani Channel, Metro Channel, Green Channel, Business Channel, Bulk Mail Channel and Periodical Channel. India has one of the largest telecommunication networks in Asia.
- Apart from the urban areas more than two-thirds of the villages in India have already been covered with Subscriber Trunk Dialing (STD) telephone facility, while International communication can be made through ISD (International Subscriber Dialing).
- There is an uniform rate of STD facilities all over India. Telephone is a form of oral communication.
- It is considered very essential for the growth of commerce. It is the most preferred form as it provides instant communication.
- Mobile phone, fax and internet are the other personal communication used in the country.
Mass Communication Systems
- Mass Communication enables millions of people to get the information at the same time. It is a great way to provide education as well as entertainment
- It helps in creating awareness among the people regarding various national policies and programmes.
- The Mass Communication Systems can provide the information to people in two methods. They are Print Media and Electronic Media.
- Radio broadcasting in India was started in 1923 by the Radio club of Bombay. Since then it gained immense popularity and changed the social and cultural life of people. It was named as All India Radio (AIR) in 1936and again it was renamed as Akashwani in 1957.
- It broadcasts a variety of programs related to information, education and entertainment. Special news bulletins are also broadcasted on special occasions like session of parliament and state legislatures.
- Television broadcasting has emerged as the most effective audio-visual medium for disseminating information and educating the masses. Television network in India is known as Doordarshan (DD)which started Common National Program (CNP) services and it is extended to the backward and remote rural areas.
- Internet (contraction of interconnected network)is the global system of interconnected computer networks that use the Internet protocol suite to link devices worldwide. Social media are interactive computer-mediated technologies that facilitate the creation and sharing of information, ideas, career interests and other forms of expression via virtual communities and networks.
- With over 460 million internet users, India is the second largest online market, ranked only behind China. By 2021, there will be in India about 8 million internet users.
- Despite the large base of internet users in India, only 26 percent of the Indian population accessed the internet in 2015.
- This is a significant increase in comparison to the previous years, considering the internet penetration rate in India stood at about 10 percent in 2011.
- Furthermore, men dominated internet usage in India with 71 percent to women’s 29 percent.
Print Media

Newspapers are the most common but powerful means of communication come under print media. India has many newspapers which carry information on local, national and international events to the people.
Satellite Communication

- The use of Satellite in getting a continuous and synoptic view of larger area has made this communication system very vital for the country.
- Satellite images are used for weather forecasting, monitoring of natural calamities, surveillance of border areas etc.
- The communication through satellites emerged as a new era in communication in our country after the establishment of Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) in 1969.
- Satellite system in India can be grouped into two-the Indian National Satellite System (INSAT) and the Indian Remote Sensing Satellite System (IRS).
- The INSAT, established in 1983,is a multipurpose system for telecommunication, meteorological observation and for various other programs.
- The INSAT series are used for relaying signals to television, telephone, radio, mobile phone It is also useful in weather detection, internet and military applications.
- The INSAT series, GSAT series, KALPANA-1, HAMSAT, EDUSAT are the major communication satellite used for communication purpose.
- GSAT–7A is the recent launch (December 19, 2018)for communication programs. INSAT-1B launched on 30th August 1983 is the first communication satellite in INSAT series.
- Trade is an important phenomenon that decides the economic growth of a country. Trade is an act (or) process of buying, selling or exchanging of goods and services.
- The primitive method of trade was known as the Barter system where goods were exchanged for goods.
- Later on, money was introduced as a medium of exchange in buying and selling of goods.
- The difference in value between the imports and exports is called balance of trade.
- The situation in which the value of exports exceeds the value of imports is termed as favourable balance of trade and the reverse position is termed as unfavourable balance of trade.
Types of Trade
- Trade in general, is of two types. They are Internal and International.The trade carried on within the domestic territory of a country is termed as Internal trade. It is also called as Domestic trade or Local trade.
- Land transport (roadways and railways) plays a major role in this trade. Local currency is used in internal trade. It helps to promote a balanced regional growth in the country i.e, tea from Assam, coffee from Karnataka, Rubber and spices from Kerala, minerals from Jharkhand etc.,are supplied to different parts of our country.
- Trade carried on between two or more countries is called International trade. It is also called as external trade or foreign trade.
- Export and Import are two components of International trade. Export means goods and services sold for foreign currency. Import means goods and services bought from overseas producers.
- Waterways and Airways play a vital role in this type of trade. Foreign currency is involved in international trade. The trade between any two countries is called Bilateral trade.The trade between more than two countries is called Mutilateral Trade.
Exports

The major exports of India are tea, marine products, ores and minerals, leather products, gems and jewels, sports goods, chemicals and related products, plastics and rubber articles, articles of stones, plaster, cement, asbestos, mica, glass ware, paper and related products, base metals, optical, medical and surgical instruments, electronic items, machinery, office equipments, textiles and allied products.
Imports
The major imports are petroleum products, pearls, precious stones and semi-precious stones, gold and telecom instruments.
India’s Trade Performance
- The volume of India’s foreign trade has increased many fold since independence. During 2008 -2009, the volume of trade was 840755 crores and it rose to 1039797 crores in 2016-2017.
- The import during 2008-2009 was 1374436 crores and was with a deficit of 40679 crores.
- The import during 2016–2017 rose to 1396352 crores and was with the deficit of 356555 crores.
- It reveals that not only the balance of trade is unfavourable but also the increase in the level of deficit.
More to Know:
- In 2007, the Government of India merged the Air India and Indian Airlines under National Aviation Corporation of India Limited (NACIL). In which NACIL (A) provides international services, NACIL (I) provides domestic services and services to neighboring countries in south east Asia and middle East.
- The state of Meghalaya has no railway network.
- The first sub-urban railway was started in 1925 in Mumbai. Chennai becomes the sixthIndian city with metro railway. Gatiman Express is the fastest operational train in India. This train connects New Delhi and Agra and touches 160 km/h. This train takes a travel time of 105minutes to cover 200km journey.
- The first train steamed off from Mumbai to Thane in 1853, covering a distance of 34 km. In 1951, the systems were nationalized as one unit “The Indian Railways”.The headquarter of Indian Railways is New Delhi.
- National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) was established in 1995. It is an autonomous body under the Ministry of Surface Transport.
- Shershahsuri built the shahi (Royal) road to strengthen and consolidate his empire from the Indus valley to the Sonar valley in Bengal. This road from Kolkata to Peshawar was renamed as Grand Trunk(GT) road during the British period. At present, it extends from Amristar to Kolkata. It is bifurcated into 2 segments: (a) (NH)-1 from Delhi to Amristar, and (b) NH-2 from Delhi to Kolkata.
- The ratio between the economically active and economically inactive of population is termed as Dependency Ratio.
- In India the first census was carried out in the year 1872.But the first complete and synchronous census was conducted in 1881.And the 2011 census represents the fifteenth census of India.
TRANSPORT AND COMMUNICATION IN TAMIL NADU
Roadways
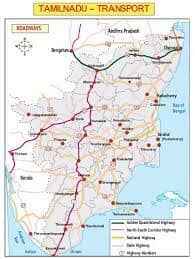
- Of all the States of India, Tamil Nadu has a sound network of roads. All economic sectors of the State is inter connected and interlinked by roadways.
- The State Transport Corporations operate the public transport system along with private transport organizations. Compared to other States of India, Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporations operate bus services in a fullfledged, facilitating manner.
Roadways may be classified into four types. They are:
- National Highways;
- State Highways;
- District roads; and
- Village Roads.
There are 24 National Highways covering a total distance of 4500km. Golden Quadrilateral Project. To meet the ever increasing demand from public, there are seven transport corporations functioning in the State. They are given below with their area of operation:
- Metropolitan Transport Corporation-Chennai and sub urban areas – Chennai as head quarters.
- Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporation-Villupuram(Cuddalore, Vellore, Tiruvannamalai, Kanchipuram and Tiruvallur districts with Villupuram as head quarters).
- Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporation- Kumbakonnam(Thanjavur, Thiruvarur, Nagapattinam, Karaikkal(Puducherry) Thiruchirapalli, Karur, Perambalur, Sivagangai, Ramnad and Pudhukottai districts with Kumbakonam as head quarters).
- Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporation-Salem(Salem, Dharmapuri, Namakkal and Krishnagiri districts with Salem as head quarters).
- Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporation- Coimbatore(Coimbatore, Trippur, Erode and the Nilgiris districts with Coimbatore ass head quarters).
- Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporation – Madurai(Madurai, virudhunagar, Dindigul and Theni districts with Madurai as head quarters).
- Tamil Nadu State Transport Corporation- Thirunelveli(Thirunelveli, Thuthukudi, Kanyakumari districts with Thirunelveli as head quarters).
Table: Length of roads in km
| Length of roads | (in km.) |
| 1. National Highways 2. State Highways 3. Corporation and Municipalities 4. Town Panchayat Roads 5. Village Oanchayat Roads 6. Panchayat Union roads 7. Forest Roads |
4,500 5,525 17,161 15,591 63,538 32,791 3,930 |
- Apart from these the State has vehicular transport in the form of two and three wheeler vehicles which constitute about 83.9%. The number of registered vehicle population in Tamil Nadu had increased to 10.064 million in 2007-08.
- There are 64 vehicular zones in the States. Among the Regional Transport Offices, Chennai is the largest one which has – 61 centres.
Tamil Nadu Roadways

Recent Developments in Road Transport
- Conversion of single lane of State Highways into double lane and multilane.
- The wideningand improvement of road from Madhyakailash in Adyar to Siruseri on Old MahabalipuramRoad(OMR) for about 24km was laid. This is referred to as IT Expressway and it serves as connectivity to all IT companies.
- The East Coast Road(ECR) that is built along the coast of the Bay of Bengal connects Chennai and Cuddalore via Pondicherry. It gives rise to spectacular scenic views with beaches and fishermen hamlets. Presently, the East Coast Road has been extended to Thuthukudi via Chidambaram, Nagapattinam and Ramanathapuram.
- The Golden Quadrilateral Project of the National Highway Development that runs for about 1,232 km in Tamil Nadu has been completed.
- Most of the mofussil traffic had been diverted on to the byepass roads to avoid traffic congestion.
- CMBT(Chennai Mofussil Bus Terminus), which is the largest modern bus terminus in Asia, Koyambedu, Chennai has been established.
- Bridges and flyovers have been constructed in many districts of Tamil Nadu along the National Highways. Some of the notable ones may be found in Chennai City-Chennai Airport Flyover, Perambur Flyover, Anna Flyover and Kathipara junction Flyover. In Vellore, Tindivanam and Ulundurpet flyovers have been constructed to ease vehicular traffic congestion.
- Ring roads that encircle urban areas to divert vehicular traffic to avoid traffic passing through the centre have been implemented.
- SETC operates a variety of buses, namely, semi-deluxe, super-deluxe, video coach, ultra-deluxe, Volvo-deluxe and air suspension buses within Tamil Nadu an adjacent States.
Railways
Tamil Nadu is well served with a good network of railways as part of the southern Railways with headquarters at Chennai. Rail tracks are classified into:
- Broad gauge
- Metre gauge
- Narrow gauge
- Suburban Railway
In Tamil Nadu the total length of railway tracks is about 5,952 km and total number of railway stations is 532 to connect all the major cities of Tamil Nadu.
Tamil Nadu Railways

- The Southern Railways zones have been demarcated into six divisions, namely, Chennai, Madurai, Salem, Palakkad, Thiruvanathapuram and Thiruchirappalli. Main rail kunctions in the State are:
- Chennai, Erode, Coimbatore, Thirunelveli, Madurai, Thiruchirappalli and Salem.
- Chennai has a well established suburban railway network, with three different lines connecting Chennai with Arakkonam, Gummidipoondi and Chengalpattu, MRTDS Railway line connects Chennai Beach to Velachery.
Recent developments in railways
- The metre gauge rails are being converted into broad gauge of which 26% of the length had been electrified.
- Gauge conversion project has also been taken up from Chennai Beach to Tambaram, Chengalpattu and other suburban areas.
Waterways
- Waterways are the cheapest means of transport. It may be divided into inland waterways and seaways. The State has 1000 km of coastline.
- The three major ports of Tamil Nadu are Chennai, Thuthukudi and Ennore. They play a crucial role in the provision of infrastructural support in the State.
- Minor Ports are anchorage ports where cargo is transhipped from the vessel to the shore. Some of the minor ports are Cuddalore, Nagapattinam, Kolachal and Rameswaram.
| Cargo handled by major ports | |
| Ports Chennai Tuticorin Ennore |
(in million tonnes) 57.15 21.62 11.56 |
Projects Under Progress Sethusamudram Shipping Canal Project (SSCP)
- It aims at creating a navigation channel from the Indian ocean to the Bay of Bengal through Gulf of Mannar, Adam’s Bridge, Palk Bay and Palk Strait within the Indian Border.
- This project is of strategic importance as it connects the neighbouring Continents and countries. It also acts as a catalyst for industrial development, super trade and commerce advance coastal shipping and generate employment.
Tamil Nadu – Major Seaports and Airports
- Buckingham canal that once connected Marakkanam in villupuram with Vijayawada in Andhra Pradesh has lost its importance.
- Vedaranyam canal that connects Vedaranyam and Nagapattinam and has also lost its importance.
Airways
- Airways is the fastest and costliest means of transport which can carry passengers, freight and mail. They connect local, regional, national and international cities.
- Tamil Nadu has a major international airport, which is named as Anna international Airport. It is connected to 19 countries and operating more than 169 direct flights every week.
- This is currently the third largest airport in India after Mumbai and Delhi.
- Chennai has direct air services to Sri Lanka, Dubai, Germany, Indonesia, Malaysia, England, Maldives, Saudi Arabia and Singapore.
- The air services that operate between Chennai and Coimbatore through Salem promote the industrial development of Salem and Mettur.
International Airports
- Chennai (Anna)
- Coimbatore
- Thirucirappalli
Domestic Airports
- Chennai (Kamarajar)
- Madurai
- Salem
- Tuticorin
| Airports | Cargo handled (in tonnes) |
| Anna International (Chennai) Kamarajar Domestic(Chennai) Coimbatore Madurai Thiruchirappalli |
2,27,704 42,905 1,858 375 238 |
Communications
- The means through which ideas and information are exchanged are called “called of Communication”.
- They are Personal Communication and Mass Communication Networks Personal Communication includes Postal Services, Telegram, Telephone, Internets, E-mail and Fax Mass Communication Network is carried on by the Government agencies.
- They are: Print Media (books, Journals, magazines and newspapers) and Electronic Media (Radio, Television, Telecommunications, Mobile phone, E-mails, E-commerce and Teleprinter).
Postal Network and Telegraph
Tamil Nadu has four postal districts, namely:
| Zone/ Districts | Headquarters |
| Chennai Western Central Southern |
Chennai Coimbatore Thiruchirappalli Madurai |
- The postal Department has allocated the Postal Index Number (PIN) to facilitate faster delivery of letters in the form of Air Mail Service, Railway Mail Service and Speed Post.
Postal and Telegraph offices in Tamil Nadu
- Number of Post Offices alone: 12,115 Number of Post and telegraph offices : 3,504.
- In India the BSNL is a major service provider. Direct calls can be made across the country and the world with STD(Subscriber Trunk Dialing), PCO(Public call office) and ISD (International Subscriber Dialing) facilities respectively. Today,
Tamil Nadu has :
- Telephone exchanges- 2,408
- Telephone subscribers – 33,46,906
- There is no Telegram service at present.
- The private basic telecom services are provided by BharatiInfotel, TATA, Reliance, Airtel, Aircel, Vodafone, Uninor.
Telecommunications
Telecom growth has intimate relationship with the IT sector. The State has witnessed a boom in the number of PCOs and the landline segment. Rapid expansion in the telecom sector is accompanied by simultaneous significant technological changes. Cell phones are one such advancement in the field of technology. Even the internet can be accessed using cell phones. The world is shrinking with increasing spread of the communication network. The following are the services provided by the BSNL:
Cellular Subscribers (Cumulative in Lakhs)
| Year | Tamil Nadu | All India | Percentage share to All India | |
| 2002-03 2003-04 2004-05 |
6.15 16.28 33.53 |
126.88 261.5 410.2 |
4.85 6.2 8.17 |
|
| The total number of cellular phones in use in Tamil Nadu: 3337087 | ||||
- Internet is provided to subscribers in the name of Data One Broadband.
- Both post-paid and prepaid cell phone services are offered through public as well as private service providers
All India Radio (AIR)
Indian radio broadcasting, which was started in 1927, became All India Radio(AIR) in 1936. AIR has 15 Radio Stations in Tamil Nadu. Private Broadcasters have set up FM Radio Stations and broadcast a variety of programmes on education, agriculture and entertainment.
Doordharshan
It is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world. All the major live telecasts of national and international programmes bring the viewers under one roof. It transmits education all programmes for Schools and Universities through “Edusat”.
Internet and Intranet
- The present world is networked with the World Wide Web, known simply as the internet and Intranet. Of the two, internet plays an important role in the field of education and transfer on knowledge. Internet can be accessed by any individual from any part of the world.
- An Internet is a private computer network. Intranets are websites that can only be accessed within a company through their internal network.
Satellite
- It is the latest means of communication which has brought revolution in communication all over the world.
- India’s communication network is operated through two satellites, namely, Indian National Satellite (INSAT) and Indian Remote Sensing Satellite(IRS).
- These two, apart from communications, assist in the prediction of meteorological events and natural resources management.
Print Media
It is another powerful medium to convey information through various news agencies of India that are operating under the umbrella-Press Trust of India, United News of India and Press Information Bureau.
Communication Technology and its advantages
- It plays a vital part not only in personal life but also important role in business and education through satellites.’
- People can send and receive mails using e-mail to get information on job vacancies, admission to Universities and to obtain birth and death certificates.
- Shopping via internet(e-commerce) is a trend now-a-days.
- Telemedicine makes it possible for people in remote areas to get correct treatment at appropriate times.
- Online payment of phone bills, electricity bills and online ticket booking can also be made.
- D-Mat form of shares for share broking and video conferencing using video chat through webcam are also done using internet.
- Communication technology has developed to such an extent that even remote villages are connected to any part of the world, making the world a global village.
- GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) is a way of sending data through radio waves which is currently being used to transmit voice.
- GPS (Global Positioning System) looks like a Mobile phone which captures signals from multiple satellites and provides information on the location of a place.







